The markets of all countries are closely interconnected. When it comes to China, which imports 14 million cubic meters of softwood lumber per year, this means that only a third of the volume is consumed inside China, another third is re-exported to Europe and another third is re-exported to the United States. Accordingly, the demand in China depends on the state of the US and EU economies. In the same vein, we can talk about North Africa, bearing in mind, first of all, the Egyptian market. Unfortunately, the Moroccan market has been irretrievably lost for Russian suppliers, and negotiations on reducing duties on Russian lumber were considered meaningless. Russian manufacturers from Tunisia and Algeria were squeezed out by Scandinavian suppliers.
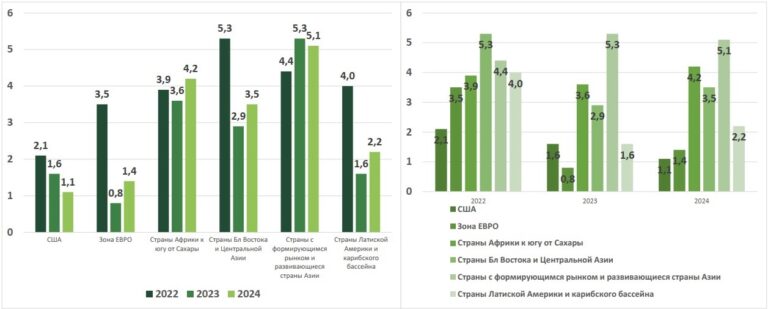
In advanced economies, the slowdown in growth is expected to be particularly significant, from 2.7 percent in 2022 to 1.3 percent in 2023. In a likely alternative scenario, the growth rate of the global economy will decrease to about 2.5 percent in 2023, while in advanced economies the rate will fall below 1 percent. Thus, the main driver of the development of the global economy will be developing countries, including China.
China is the leader in the global consumption of lumber, which is facing serious problems. These problems relate primarily to the real estate market, which is the main driver of demand for lumber in any country.
The real estate market in China is experiencing a downturn: sales of new homes by large developers fell by 29% in September 2023 compared to September 2022. A number of the largest Chinese developers have experienced long-term financial difficulties, and investments in the industry are declining. In January-September 2023, investments in real estate development amounted to 8726.9 billion RMB, which is 9.1% less than a year earlier. Of these, investments in residential buildings amounted to 6627.9 billion RMB (76% of the total investment in real estate), a decrease of 8.4%.
China’s exports are declining, and tensions with the West, led by the United States on trade and technology issues, persist.
Local governments need to take more stimulus measures to ensure a stronger and longer-lasting economic recovery. In this regard, economists expect a difficult transition period for the Chinese economy.
Imports of softwood sawlogs to China, in the first eight months of 2023, decreased by 7.9% and amounted to 20.5 million m3 compared to the same period last year. The largest suppliers (according to Timber-Online) were: New Zealand, Germany, USA and Poland. Germany and Poland export spruce logs damaged by bark beetle to China.
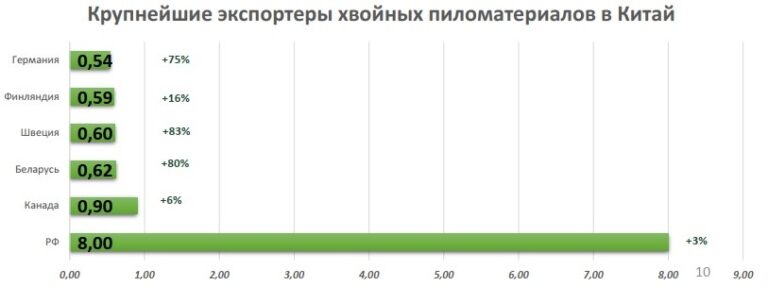
Imports of softwood lumber to China in the first eight months of 2023 increased by 11.8% (to 12.3 million m3) compared to the same period in 2022. The six largest supplier countries compared to the same period in 2022 (according to Timber-Online) were: Russia, Canada, Belarus, Sweden, Finland, Germany. Moreover, the supply of Russian products prevails.
Chinese buyers are ready to buy large volumes in Russia, they are ready to pay good prices for high-quality lumber, but there is a question of supply diversification. The decrease in the rate of lumber consumption is reflected in Russian exporters. First of all, small and medium-sized manufacturers suffer, large ones that can control the high quality of their products, ensure large and stable supply volumes will remain active in the Chinese market.
One of the trends in China is the change in the centers of wood consumption. The centers began to leave Taicang inland, where goods can be delivered exclusively by rail. At the same time, there is both a reduction in consumption and a reduction in stocks in warehouses in China.
Another index that makes sense to pay attention to is the purchasing directors’ expectation index from the Chinese economy or the so–called “purchasing directors in China’s manufacturing industry” index (PMI). In October 2023, it was 49.5% (below the threshold), down 0.7% from the previous month, indicating that the level of business activity in the manufacturing industry decreased during the month. For large enterprises, the business activity index was 50.7% (-0.9%). For medium-sized enterprises, it was 48.7% (-0.9%). For small enterprises, it was 47.9% (-0.1%).
Among the five sub-indices that make up the PMI: the production index was 50.9% (-1.8%), the index of new orders was 49.5% (-1.0%), the main index of raw materials stocks was 48.2% (-0.3%), the indicator of supplier delivery time was 50.2% (-0.6%), the index of employment was 48.0% (-0.1%). If we decipher this indicator, then if it is more than 50%, the economy will grow, if less than 50%, then it will fall.
All this suggests that there will be no improvement in China in 2024, in terms of domestic consumption. As mentioned earlier, domestic consumption in China is only 30% of the imported volume. The rest is re-exported to the EU and the USA. But in the EU, except for Spain, the index of the number of permits issued for the construction of new houses has a pronounced negative trend. In addition, the number of bankruptcies in Europe of companies in the construction industry has doubled over the past year. That is, it is obvious that 2024 will not be the year of increased consumption of lumber for construction, and therefore for furniture.
According to reviews by EUWiD, Fordaq and Timber Industry News, a general slowdown in the growth rate in the timber and woodworking industries is observed in many European countries. The slowdown in growth is influenced by various economic and industry factors. All this suggests that the Chinese are forced to buy less in Russia.
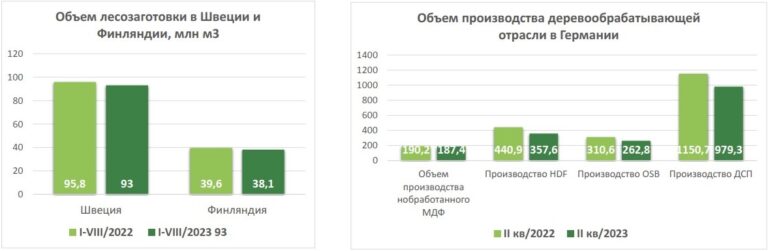
According to EUROCONSTRUCT, the European construction industry is expected to experience minimal growth in the coming years, which puts a lot of pressure on the sawmill industry. The market for wooden products in the Nordic countries is in a state of stagnation, and demand decreased in the third quarter of 2023. After two successful years with exceptionally high product prices and profits, the Northern European forestry industry is now at the bottom of the business cycle. The industry reacted sharply to the situation by limiting production – stocks were reduced and price increases have already been announced in some sectors. However, price growth is still constrained by high supply, and demand-side problems persist.
The export opportunities of Scandinavian manufacturers to the Middle East, North Africa and China are weak. The difficult market situation for sawmills will continue. If further weakening of the global economy follows, then most of the sawmills in Northern Europe may not be able to cope with the situation. Last summer, a weak market, combined with historically record high commodity prices, contributed to the temporary closure of production facilities.
In the USA, a key indicator of the state of the market of building materials and materials for furniture production is the indicator of the volume of housing commissioning. In 2023, from month to month, this indicator fluctuates +/- near zero. However, it remains below the level of 2022.
According to the September 2023 housing construction forecast, the volume of housing starts will decrease in 2023 by 2022 and continue to decline in 2024.
Mortgage rates have risen above 7%, which has made housing significantly less affordable for many buyers. Market data point to growing sales in the secondary housing market, which, however, are 15.3% lower than the same indicator last year.
Low sales volumes will have a negative impact on the lumber and slab markets in both 2023 and 2024.
Another indicator indicating a difficult situation is unemployment. According to the estimate of the Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia in the third quarter of 2023, unemployment will average 3.6% in 2023. The forecast for 2024-2026 ranges from 4.0% to 4.2%.
The production of softwood lumber in the United States, in the first seven months of 2023, decreased by 2.5% (to 22.1 billion MBF) compared to the first seven months of 2022. The volume of lumber production in Canada decreased by 10.3% in the first seven months of 2023.
Prices for hardwood lumber in the United States began to fall sharply in the summer of 2022 and continued to decline until recently, reaching a minimum, but without increasing demand.
Domestic and global demand continues to be constrained by excess inventories and high interest rates. The annual estimate of the use of hardwood lumber in 2023 decreased by 22.9% compared to 2022, which is the lowest figure in the entire history of observations.
In North Africa, and above all Egypt, no economic growth is expected. The export of lumber to Egypt in 2013 is estimated at 502,000 m3. And, in our opinion, the volume will not rise above 450,000 m3 in 2024.
As for Russia, as you know, the statistics do not include the production volumes of saw mills. These volumes will prevail in supplies to Central Asia and Iran. In these markets, low price is preferred over the quality of lumber. In Uzbekistan, after all, as in Russia, there is a division into a quality product and a non-quality product, but Uzbekistan is heavily overstocked. So far, there are large residues in warehouses, which has led to a decrease in prices. Uzbekistan offers prices less attractive than even in the Russian market.
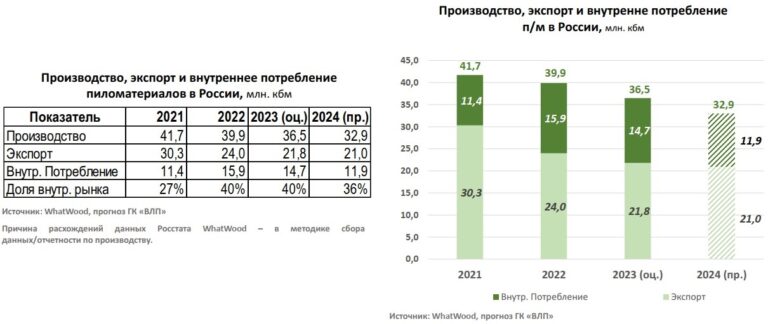
We predict that in 2023 the volume of sawn timber production in Russia will be 36 million m3 in 2023 and in 2024 a decrease to 33 million m3, which will be associated with a reduction in logging due to the high risks associated with plywood production, since entering the plot it is necessary to harvest not only a sawlogs, but also a logs for veneer (e.g. birch), against the background of problems related to plywood sales. Despite the shortage of softwood, uncertainty in the market will not stimulate logging.